The work of a load balancer is to distribute traffic among multiple instances of the applications or across multiple servers. The load balancing aims to ensure that excess traffic doesn’t cause downtime of your systems or applications. The load balancer is like a pressure valve that lets the pressure of requests or traffic load spread out to other chambers (here servers or multiple instances of the application.
Google Cloud Load balancing uses the same frontend infrastructure on which Google operates. It processes 1 million +queries per second entering from 80+ global load balancing locations. Query processing is done with excellent performance and minimum latency. It is a distributed managed service.
Google Cloud Load Balancing Features
– External and Internal Load balancing
External load balancing takes place for online applications. The types of external load balancing include
- External HTTP/S Load Balancing
- SSL Proxy Load Balancing
- TCP Proxy Load Balancing
- External TCP/UDP Network Load Balancing
Internal load balancing is done for clients inside the Google Cloud. The types of internal load balancing include
- TCP/UDP Load balancing
- Internal HTTP/S load balancing
Ready to experience the full power of cloud technology?
Our cloud experts will speed up cloud deployment, and make your business more efficient.
Layer 4 of Google Cloud Load balancing enables routing traffic based on network and transport layer protocols data such as TCP, ESP, UDP and ICMP. Layer 7 enables load balancing by sending requests for routing decisions (Uses attributes like HTTP header and URI)
– Load balancing is software-defined
The load balancing activity is not based on any instance or device. That way, you are not locked in any physical constraints for load balancing like load balancing infrastructure. You are free from traditional challenges of the load balancing based on an instance, like scale and others
– Autoscaling
Google Cloud load balancing helps you to scale easily when traffic and users grow. The demand spikes are automatically addressed by diverting traffic to different regions of the world to various servers. Within seconds, you can scale from zero traffic to total traffic.
– Multiple regions load balancing
To meet the demands of high availability, the load-balanced resources can be distributed in multiple regions.
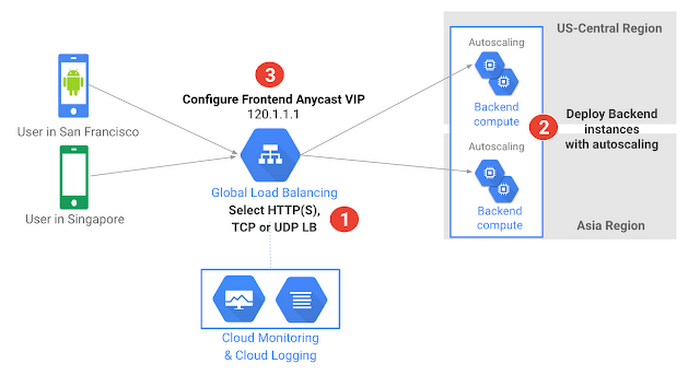
– Single Anycast IP address
With Google Cloud Load Balancing, a single anycast IP address acts as the frontend for all your instances (backend) globally.
– Advanced Support
Google Cloud Load Balancing has advanced support features like
- IPv6 global load balancing
- Web Sockets
- Request headers (user-defined)
- Protocol forwarding (for private VIPs).
- Integration with Cloud CDN
- Integration with Google Cloud Armor (for protection against threats)
To get the first free consultation on migrating cloud services, click here.








